Introduction to Spatial Design in Warehouses
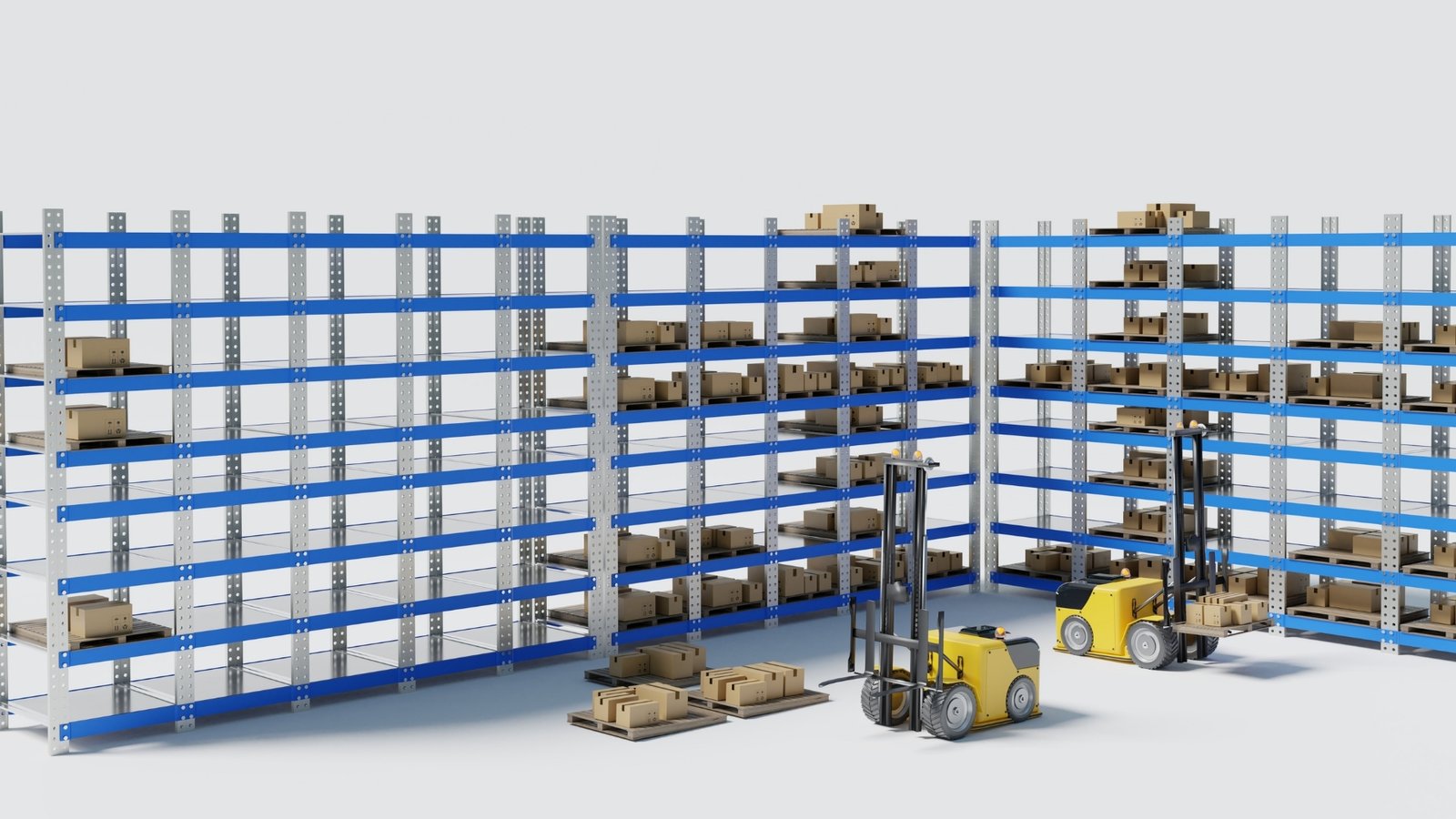
Spatial design in warehouses refers to the strategic arrangement and organization of physical spaces to optimize functionality and efficiency in logistics operations. This concept plays a crucial role in ensuring that the flow of goods and materials within a warehouse is both streamlined and effective. By carefully planning the layout of shelving, storage areas, and work zones, spatial design can significantly impact the overall performance of warehousing facilities.
At its core, spatial design encompasses various elements, including the positioning of storage systems, the width of aisles, and the allocation of workspaces. These considerations are integral to maximizing warehouse efficiency, as they influence how well personnel can navigate the space while minimizing time wasted in unnecessary movement. For instance, a well-designed layout can facilitate quick and easy access to frequently used items, which is essential for maintaining productivity in a fast-paced environment.
In the context of logistics, effective spatial design not only enhances the speed of operations but also supports safety and compliance. Properly defined zones can reduce the risk of accidents and ensure that safety protocols are adhered to, ultimately leading to a more secure working environment. Additionally, spatial design can incorporate advanced technologies, such as automated storage and retrieval systems, which further streamline processes and optimize space utilization.
Understanding the importance of spatial design in warehouses is essential for logistics professionals aiming to enhance operational efficiency. As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of innovative designs and technologies will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of warehouse management. By embracing the principles of effective spatial design, organizations can significantly improve their logistics capabilities and respond more adeptly to the demands of the market.
Understanding Warehouse Efficiency
Warehouse efficiency refers to the ability of a warehouse to optimize its operations while minimizing costs and enhancing productivity. It is a critical aspect of logistics management that directly impacts the overall supply chain performance. Measuring warehouse efficiency involves utilizing various key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect operational capabilities, resource utilization, and service levels.
One prominent metric for assessing warehouse efficiency is order picking speed. This measure indicates how quickly items can be retrieved from storage locations to fulfill customer orders. A higher order picking speed can significantly reduce lead times, thus improving customer satisfaction and retention. Additionally, improving this metric often involves streamlining workflows, implementing advanced picking technologies, and optimizing shelf layouts to facilitate faster access to products.
Inventory turnover is another vital indicator of warehouse effectiveness. This metric assesses how often the inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period. A high inventory turnover rate suggests that products are moving quickly through the warehouse, which typically reflects effective inventory management practices. Efficient inventory turnover not only reduces holding costs but also minimizes the risk of obsolescence, ensuring that the warehouse operates without excess stock.
Space utilization, which examines how effectively warehouse space is organized and utilized, is equally important. Effective spatial design can maximize storage and operational areas, leading to greater efficiency. By employing sophisticated racking systems, maintaining clear pathways for movement, and using vertical space effectively, warehouses can significantly improve their capacity and streamline operations.
In summary, understanding warehouse efficiency is essential for logistics success. By focusing on crucial metrics such as order picking speed, inventory turnover, and space utilization, logistics professionals can identify areas for improvement, implement strategic changes, and ultimately drive better performance in warehouse operations.
Key Elements of Spatial Design
Efficient spatial design in warehouses plays a crucial role in maximizing productivity and streamlining operations within the logistics sector. The foundational aspect of an effective warehouse design is the layout strategy employed. Common approaches include grid, flow-through, and dynamic storage systems. A grid layout is characterized by its straight aisles and uniform shelving, allowing easy navigation and systematic storage. Conversely, flow-through systems facilitate the movement of goods from one end of the warehouse to the other, ensuring quick access to inventory. Dynamic storage systems incorporate adjustable shelving and automated solutions that adapt to varying inventory levels, thus enhancing space utilization.
Another vital consideration in spatial design is aisle width. The dimensions of aisles directly impact the efficiency of material handling processes. Wider aisles may accommodate larger equipment and improve maneuverability, while narrower aisles can optimize space use. However, a careful balance between aisle width and storage density must be maintained to ensure that personnel and machinery can operate effectively without compromising safety and accessibility.
Moreover, the choice of shelving types and storage methods significantly influences warehouse efficiency. Various shelving options, such as selective, push-back, or pallet flow shelves, cater to different inventory needs and picking strategies. Selective shelving, for instance, provides immediate access to all items but may require more floor space, while push-back and pallet flow options maximize storage density but necessitate a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory management approach.
Incorporating these key elements—layout strategies, aisle width considerations, shelving types, and storage methods—ultimately results in a comprehensive understanding of an efficient warehouse design. This knowledge is essential for logistics professionals aiming to optimize operations and enhance overall productivity within their warehouses.
The Role of Technology in Spatial Design
In the contemporary logistics landscape, technology plays a critical role in enhancing spatial design within warehouses. Advances in Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) contribute significantly to optimizing the layout and operational efficiency of logistics facilities. These systems streamline warehouse processes, enabling operators to manage inventory levels, order fulfillment, and space utilization efficiently. By employing a robust WMS, businesses can adapt their spatial arrangements to meet fluctuating demands while minimizing downtime and maximizing throughput.
Automation technologies further revolutionize spatial design in warehouses. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), robotics, and conveyor systems facilitate seamless movement of goods across the storage facility. These innovations allow for more dynamic spatial configurations that can be adjusted in real-time based on operational needs. The use of automation not only increases efficiency but also enhances safety by reducing the risk of human error during material handling.
Data analytics emerges as another cornerstone in the integration of technology and spatial design. By harnessing real-time data, organizations can make informed decisions about warehouse layout and operations. Advanced analytics tools enable managers to assess inventory patterns, identify bottlenecks, and forecast demands. This capability is crucial for optimizing space allocation and workflow, ensuring that logistics operations remain agile and responsive to market changes.
Moreover, the continuous evolution of technology ensures that warehouses can adopt more sophisticated design strategies. Integrating Internet of Things (IoT) devices allows for real-time tracking of assets throughout the facility, which aids in reducing losses and enhancing inventory accuracy. This technology not only promotes seamless operational efficiency but also supports improved strategic planning and resource allocation.
In summary, the incorporation of technology into spatial design significantly elevates warehouse efficiency in logistics. By leveraging advancements in WMS, automation technologies, and data analytics, businesses can create adaptive and effective spatial configurations that optimize operations and overall performance.
Practical Examples of Effective Spatial Design
The impact of spatial design on warehouse efficiency is best understood through real-world examples showcasing the success achieved by various industries. One notable case is Amazon, which utilizes advanced spatial design techniques including optimized shelving layouts and strategic placement of high-demand items. By employing zone storage, Amazon effectively reduces picking time and enhances inventory management. Their design employs vertical space to maximize storage, allowing for increased throughput while maintaining accessibility.
Another illustrative case can be found in the automotive industry, specifically Toyota. Toyota has implemented the Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory system alongside effective spatial design principles. The company structures its warehouses to accommodate quick access to parts, thereby minimizing wait times in assembly lines. Their use of modular designs and flexible shelving not only allows for easy reconfiguration as demand changes but also supports improved flow of materials, further driving efficiency in operations.
The distribution company, Walmart, offers another example of spatial design’s efficiency. By adopting a cross-docking method, Walmart minimizes storage time and maximizes the speed of inventory turnover. Their facilities are designed to allow for seamless transfer of goods from inbound to outbound trucks without intermediate storage, thus reducing handling time and enhancing overall operational efficiency. The strategic layout of their transportation routes within the warehouse further facilitates quick access to both incoming and outgoing items.
These examples illustrate the importance of spatial design within warehouse settings. They underscore the necessity for companies to invest in thoughtful design to foster efficiency. By analyzing successful cases like Amazon, Toyota, and Walmart, it becomes evident that effective spatial design not only boosts performance and productivity but also contributes to greater satisfaction among employees and customers alike. Adopting similar strategies can yield significant benefits for warehouses across various sectors.
Measuring the Impact of Spatial Design on Efficiency
Measuring the impact of spatial design on warehouse efficiency is essential for optimizing logistics operations. By employing various performance metrics and quantitative analysis methods, organizations can assess how changes in warehouse layout directly influence productivity and overall efficiency. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as order fulfillment time, inventory turnover rate, and space utilization are fundamental metrics used in this evaluation process.
One prevalent approach involves conducting time-motion studies, which analyze how long it takes for employees to complete specific tasks in different warehouse setups. This method helps identify bottlenecks and areas needing improvement, thereby allowing for informed decisions regarding spatial design modifications. Additionally, other quantifiable measures, such as cubic utilization rates—calculating the ratio of used space to total available space—offer insights into how effectively the warehouse environment accommodates operations.
Real-world examples illustrate the effectiveness of spatial design alterations. For instance, a warehouse that implemented a cross-docking strategy experienced reduced material handling times, leading to a significant decrease in order fulfillment times. After redesigning its layout to minimize travel distances between receiving and shipping docks, the organization noted a 20% increase in operational efficiency. Such case studies underline the profound impact of spatial design on efficiency metrics.
Moreover, pre- and post-design metrics can be invaluable for evaluating the success of a spatial redesign. Facilities can conduct thorough assessments prior to implementing changes and compare them with results after the redesign. This method allows organizations to gather data on labor productivity and capacity utilization, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of spatial design’s effectiveness in enhancing warehouse performance.
Challenges in Implementing Optimal Spatial Design
Implementing optimal spatial design in warehouses presents various challenges that can significantly influence logistics efficiency. One of the primary obstacles is space constraints. Warehouses often operate within limited square footage, which can restrict the extent to which spatial design can be improved. The challenge lies in maximizing the utility of available space while ensuring easy access to products and equipment. Consequently, careful planning and innovative design solutions are essential for overcoming this limitation, such as vertical storage options and modular shelving systems.
Budget limitations also play a crucial role in the challenges associated with spatial design. Many organizations face financial constraints that hinder the ability to invest in renovations or new technologies that could enhance warehouse efficiency. In this context, prioritizing cost-effective design strategies is vital. This may involve conducting cost-benefit analyses to determine the most impactful changes that can be made within budgetary limits. Utilizing existing resources more effectively can also yield significant improvements.
Another substantial challenge is the resistance to change exhibited by warehouse staff. Employees may be accustomed to specific workflows and could view new spatial design implementations as disruptive. To mitigate this, it is important to involve employees in the planning process. Training sessions that highlight the benefits of the proposed changes can alleviate fears and foster a culture of adaptability. Engaging staff members during transitions not only eases implementation but also leads to a more collaborative environment.
In light of these challenges, effective communication, thorough training, and strategic planning are vital. Facilities that recognize and address potential hurdles early on can establish a solid foundation for optimized spatial design, ultimately leading to improved efficiency in logistics operations.
Future Trends in Warehouse Spatial Design
As the logistics sector continues to evolve, several key trends are shaping the future of warehouse spatial design. One of the most significant trends is increasing sustainability considerations. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the need to implement eco-friendly practices, which include optimizing energy use, reducing waste, and using sustainable materials in construction. This shift toward green logistics not only minimizes environmental impact but also enhances a company’s reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has drastically redefined warehouse spatial design requirements. With the growing demand for rapid fulfillment and the personalization of shopping experiences, warehouses must adapt to accommodate varied inventory and quicker processing times. This need has led to innovative spatial solutions, such as smaller fulfillment centers strategically located closer to urban areas, allowing for quicker delivery times while optimizing the use of available space.
Flexibility and adaptability also play crucial roles in modern warehouse design. As market demands fluctuate, facilities must be designed with the capability to easily reconfigure themselves for different types of operations. This includes the modification of storage systems and the arrangement of picking areas that can respond dynamically to changing inventory trends. Therefore, scalable modular designs are becoming increasingly popular, allowing for easy adjustments without significant overhauls.
Another transformative factor is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into warehouse spatial design. AI technology facilitates better inventory management, predictive analytics, and efficient routing, which revolutionizes how warehouses are structured. Advanced robotics and automated systems, driven by AI, complement spatial designs by optimizing workflows, saving time, and contributing to overall efficiency. As logistics continues to embrace technological advancements, the incorporation of AI will be paramount in determining the future direction of warehouse spatial design.
Conclusion: The Strategic Importance of Spatial Design
In the realm of logistics, spatial design serves as a pivotal component that significantly influences warehouse efficiency. The meticulous arrangement and organization of storage spaces facilitates streamlined operations, enhancing both productivity and effectiveness. Throughout this discussion, it has become evident that an optimized spatial design not only maximizes storage capacity but also improves the flow of goods within the warehouse, directly correlating to reduced operational costs and enhanced service levels.
Furthermore, the strategic implementation of spatial design fosters an environment where swift access to inventory is prioritized. By employing techniques such as proper aisle width, carefully positioned shelving, and the integration of advanced technology, warehouse operators can significantly reduce the time spent on picking and sorting tasks. These improvements ultimately lead to quicker turnaround times and better overall responsiveness to customer demands, thereby strengthening the competitive edge of logistics operations.
Equally critical is the need for ongoing assessment and adaptation of warehouse spatial designs. The logistics landscape is in a constant state of evolution, influenced by emerging technologies, market trends, and changing consumer expectations. As a result, warehouses must remain agile and ready to reconfigure their designs to accommodate new demands and opportunities. Regular evaluations of spatial efficiency can unveil areas for improvement, ensuring that warehouses remain not only functional but also strategically advantageous.
In summary, the impact of spatial design on warehouse efficiency in logistics cannot be overstated. Through careful planning and continuous refinement, businesses can optimize their spatial configurations, thereby enhancing operational effectiveness and positioning themselves for sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive market. The strategic importance of spatial design in warehouse operations is clear; it is an essential driver of efficiency and success in the logistics sector.