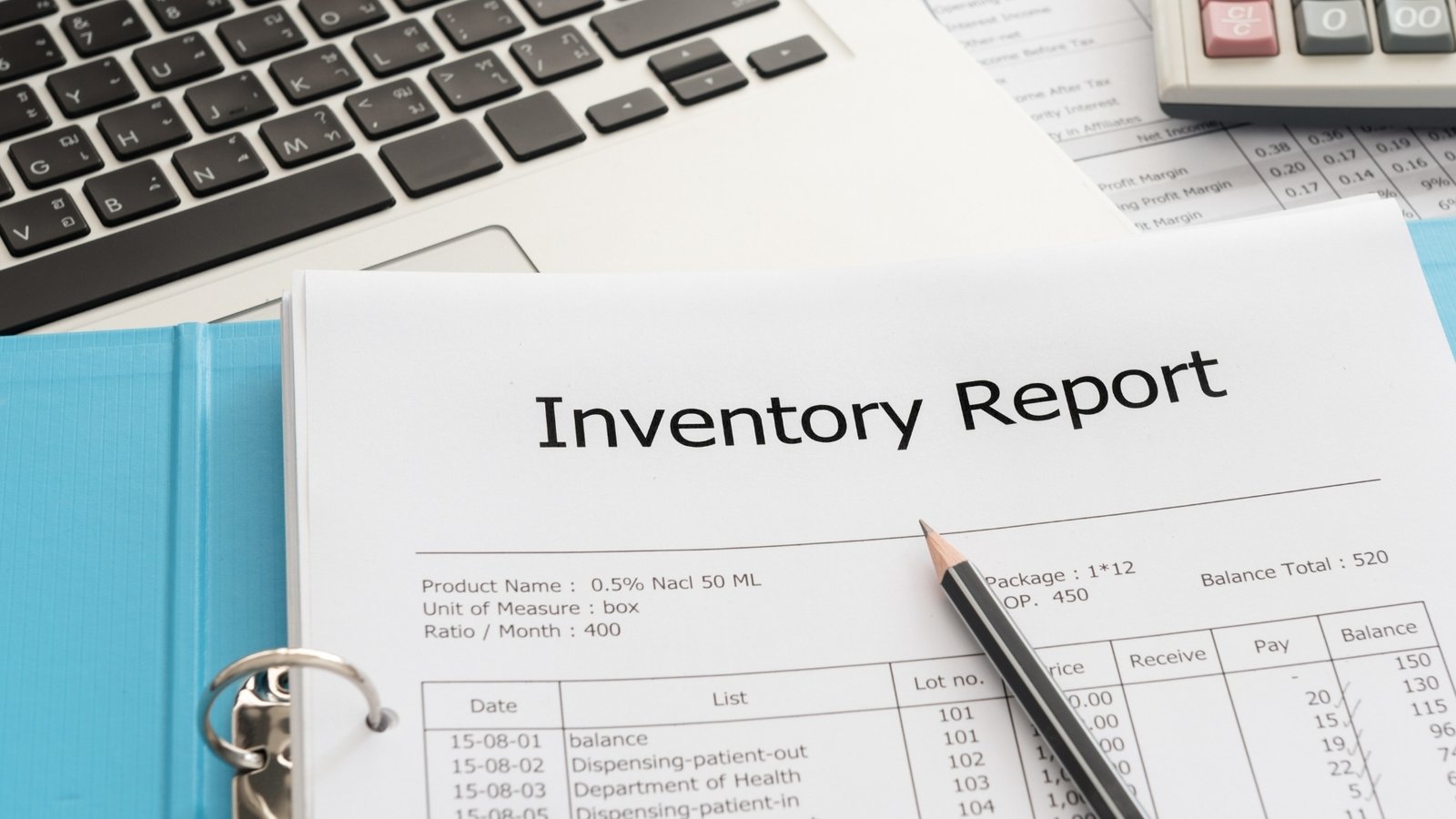
Introduction to Inventory Management
Inventory management is a systematic approach to sourcing, storing, and selling inventory—both raw materials and finished goods. It serves as a vital component of supply chain management, ensuring that businesses maintain sufficient stock levels to meet customer demands while minimizing costs associated with overstocking or stockouts. Adequately managing inventory is essential for realizing efficient operations and fostering profitability.
One of the primary objectives of inventory management is to maintain optimal stock levels. This involves a delicate balance between having enough products available to meet customer needs and minimizing the costs associated with excess inventory storage. Effective inventory management allows businesses to respond quickly to market changes and consumer preferences, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Another significant aspect of inventory management is its role in cost reduction. By implementing effective practices, businesses can decrease carrying costs, reduce waste, and mitigate risks associated with obsolete stock. This not only improves cash flow but also supports broader operational efficiency, ultimately contributing to the overall financial health of the business.
Moreover, integrating inventory management practices aligns with larger business goals, such as increasing profitability, improving customer service, and promoting sustainable operations. For example, employing just-in-time (JIT) methodologies can help companies minimize storage needs and reduce waste by synchronizing inventory acquisition with production schedules and customer demand. In this respect, inventory management is not merely an operational necessity; it is strategically aligned with the long-term vision of growth and success for a business.
Understanding Different Inventory Types
Effective inventory management is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and drive growth. One key aspect of this process is understanding the various types of inventory available, each serving a distinct purpose within the supply chain. The primary categories of inventory include raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), and finished goods. Recognizing these categories can significantly aid businesses in optimizing their inventory strategies.
Raw materials represent the basic inputs that are utilized in the production process. These items are purchased from suppliers and stored until they are needed for manufacturing. Efficient management of raw materials is essential to ensure that a business can meet production demands without incurring unnecessary costs. By maintaining appropriate levels of raw materials, companies can avoid production delays and excess inventory, which can tie up valuable resources.
Work-in-progress inventory consists of products that are in the midst of being manufactured but are not yet complete. This type of inventory includes items that have undergone some processing but require further steps before becoming final products. Managing WIP is crucial since it can reflect the efficiency of the production process. An excessive amount of WIP can indicate bottlenecks in manufacturing, suggesting that production flow is not optimized. Streamlining this type of inventory can help improve production timelines and reduce holding costs.
Finished goods are the final products completed and ready for sale. They represent the end of the production cycle and are crucial for meeting customer demand. Effective inventory management of finished goods involves balancing stock levels to meet current market needs while avoiding overstock situations that can lead to additional storage costs and markdowns. By comprehensively understanding these different types of inventory, businesses can implement strategies that enhance overall efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
The Importance of Accurate Inventory Tracking
Accurate inventory tracking is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency and drive growth. Maintaining precise records of stock levels is essential for a variety of operational aspects, from procurement to sales management. To achieve this, businesses can adopt various inventory tracking methods, including barcode systems, RFID technology, and traditional manual methods.
Barcode systems have become prevalent due to their affordability and ease of implementation. By scanning barcodes, businesses can instantly update stock levels, reducing the likelihood of human errors associated with manual entry. Furthermore, this method enables swift tracking of inventory movement, allowing businesses to respond quickly to changes in demand.
On the other hand, Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology offers advanced capabilities for inventory management. RFID tags can be read from a distance, allowing businesses to track items without needing direct line-of-sight access. This method streamlines the inventory process, reduces labor costs, and minimizes discrepancies, ultimately resulting in more robust data for decision-making.
Although manual tracking may seem outdated, it is still utilized by some businesses, particularly those with smaller inventories. However, this method is often prone to errors and can lead to discrepancies, affecting stock levels and customer satisfaction. Therefore, the transition to automated systems is highly recommended.
Implementing real-time tracking through these advanced methods significantly impacts business operations. With accurate data, companies can optimize stock levels, make informed procurement decisions, and enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability. In an increasingly competitive marketplace, investing in accurate inventory tracking systems is vital for sustaining growth and improving overall business performance.
Implementing Inventory Management Software
The integration of technology in inventory management, particularly through specialized inventory management software, has revolutionized how businesses maintain their stock levels. Utilizing such software enables organizations to improve operational efficiency, accuracy, and overall productivity, which are essential for sustained growth. One of the primary benefits of these software solutions is their ability to automate various processes, reducing human error and the time required for manual inventory tracking. Automation features, such as real-time stock updates and automatic reordering, ensure that businesses can respond promptly to changes in demand and prevent stockouts or excess inventory.
Another critical aspect to consider when selecting inventory management software is its integration capabilities. The ability of the software to seamlessly connect with existing systems, such as accounting or e-commerce platforms, plays a significant role in a business’s operational efficiency. An integrated approach allows businesses to maintain a single source of truth regarding stock levels and financial data, eliminating discrepancies that may arise from using disparate systems.
Moreover, analytics tools embedded within inventory management software provide valuable insights into inventory turnover rates, sales trends, and demand forecasting. These analytical features enable businesses to make data-driven decisions, optimizing their inventory levels while reducing costs. By utilizing such tools, companies can identify which items are underperforming and adjust purchasing strategies accordingly. This proactive approach not only helps in managing stock more effectively but also aligns inventory practices with broader business objectives.
In summary, the implementation of inventory management software is essential for businesses looking to enhance their inventory processes. By leveraging automation, integration, and insightful analytics, companies can ensure accurate stock management, streamline their operations, and ultimately support business growth.
Strategies for Forecasting Demand
Accurate demand forecasting is pivotal for effective inventory management, influencing not only stock levels but also overall business efficiency. Businesses can adopt a combination of qualitative and quantitative forecasting methods to better predict their future inventory needs. Qualitative methods often rely on expert opinions, market research, and customer feedback to gauge potential future demand. Techniques such as focus groups, surveys, and the Delphi method can provide valuable insights, especially in industries characterized by rapid changes where quantitative data may be sparse.
On the other hand, quantitative forecasting employs historical data and statistical models to generate future demand predictions. Techniques such as time series analysis, moving averages, and regression analysis are commonly used to identify patterns and trends based on past sales data. By examining historical sales figures, businesses can gain valuable insights into seasonality and peak demand periods, enabling them to adjust inventory levels proactively. For instance, a retailer may observe a consistent spike in sales during holiday seasons, prompting them to increase stock accordingly.
In addition to these methods, leveraging market trends is essential for effective forecasting. Keeping an eye on economic indicators, competitor activity, and changes in consumer preferences can provide context to demand predictions. Businesses can also employ advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to enhance their forecasting accuracy. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data, allowing for more precise predictions, and can adapt to changes in trends in real-time.
Ultimately, integrating both qualitative insights and quantitative analysis can lead to a more robust demand forecasting strategy. This holistic approach, combined with continuous monitoring and adjustment, can significantly improve inventory management and support sustainable business growth.
Establishing Inventory Control Policies
Effective inventory control policies are essential for businesses aiming to maintain efficient operations and foster growth. These policies serve as the foundation for managing inventory levels, ensuring that products are available when needed while minimizing excess stock and associated carrying costs. A well-structured inventory control framework consists of several key components, including reorder points, safety stock levels, and cycle counting.
Reorder points are critical in ensuring that inventory levels are replenished before they run too low. By calculating reorder points based on historical sales data, lead times, and desired service levels, businesses can create a proactive approach to inventory management. This allows companies to avoid stockouts, which can lead to lost sales and disappointed customers. Regularly reviewing and adjusting these levels according to seasonal fluctuations or market trends is also an important aspect of maintaining effective control over inventory.
Safety stock levels act as a buffer against variability in demand or supply chain disruptions. Determining the appropriate amount of safety stock requires an analysis of demand forecasts and supplier reliability. Striking the right balance is crucial; having insufficient safety stock can result in missed opportunities, while maintaining excessive stock ties up valuable resources.
Cycle counting, an inventory auditing procedure, is another best practice to implement within an inventory control policy. By conducting regular cycle counts, businesses can keep their inventory records accurate and identify discrepancies in stock levels proactively. This not only reinforces accountability but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that inventory management practices evolve with changing business needs.
In conclusion, establishing comprehensive inventory control policies is vital for promoting efficient inventory turnover and optimizing supply chain operations. By focusing on key components such as reorder points, safety stock levels, and cycle counting, businesses can enhance their inventory management practices, leading to improved profitability and growth. Adopting these strategies will ultimately support the long-term success of any organization.
The Role of Supplier Relationships
Supplier relationships play a crucial role in effective inventory management and can significantly impact a business’s operational efficiency and growth potential. Strong communication with suppliers fosters collaboration, which can lead to improved forecasting, timely deliveries, and a more agile supply chain. When businesses engage in consistent dialogue with their suppliers, they are better positioned to anticipate demand fluctuations and adjust their inventory levels accordingly. This proactive approach not only minimizes stockouts but also optimizes the overall inventory turnover ratio.
Trust is another vital component of supplier relationships; when businesses have confidence in their suppliers, they are more likely to establish long-term contracts that can secure favorable terms. Such arrangements can facilitate better pricing, prioritize stock availability, and ensure that businesses have access to essential materials when needed. By building trust, companies create an atmosphere where transparency can flourish, enabling quicker resolution of any issues that may arise in the supply chain.
To enhance supplier relationships, businesses should implement several strategic practices. One effective approach is to engage in regular performance reviews with suppliers, assessing their delivery times, reliability, and quality of goods or services. This practice not only holds suppliers accountable but also provides valuable feedback that can lead to improvements on both sides. Additionally, establishing joint initiatives, such as inventory management systems or shared logistics, can further streamline operations and bolster the reliability of supply chains.
In summary, establishing strong supplier relationships is not just beneficial but essential for effective inventory management. Through improved communication, trust-building, and collaborative strategies, businesses can optimize their supply chains, reduce the risk of stockouts, and ultimately support sustainable growth. A well-managed inventory system anchored by robust supplier partnerships ensures that companies remain responsive and competitive in an ever-evolving market landscape.
Utilizing Visual Inventory Management Techniques
Effective inventory management is critical for businesses seeking to enhance operational efficiency and growth. One of the most effective strategies in this regard is the implementation of visual inventory management techniques, such as Kanban and Six Sigma. These methods create a visual representation of inventory processes, thus allowing for a clear understanding of stock levels and flow throughout the supply chain.
Kanban, a methodology developed within Toyota’s production system, employs visual cues to signal the need for inventory replenishment. By using cards or boards to represent inventory items, teams can easily track stock levels and movements. This real-time visibility allows staff to make informed decisions regarding order placement, thereby preventing overstocking or stockouts. Additionally, the Kanban approach minimizes excess inventory, leading to reduced holding costs and improved cash flow for the business.
Similarly, Six Sigma complements visual inventory management by focusing on process improvement and waste reduction. By using data-driven techniques, companies can identify inefficiencies in their inventory processes. Implementing Six Sigma methodologies involves rigorously analyzing inventory workflows, enabling businesses to streamline operations and enhance accuracy in inventory counts. The visual aspects of this strategy help teams identify bottlenecks and improve their response times.
The benefits of utilizing visual inventory management techniques are multifaceted. Such techniques not only boost productivity through improved efficiency but also significantly reduce waste. This leads to a more sustainable business model by minimizing excess orders and wasteful practices. Moreover, staff are empowered with enhanced visibility and can engage in quicker decision-making, which is essential in adapting to dynamic market conditions. Overall, integrating visual management tools can streamline inventory processes, thus driving long-term business growth.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
In the dynamic landscape of commerce, effective inventory management practices are paramount for sustainable business growth. Continuous improvement and adaptation are critical components that empower businesses to enhance their inventory strategies and respond responsively to evolving market conditions. Embracing a mindset of ongoing refinement allows organizations to not only meet current demands but also to anticipate future trends.
Measuring the effectiveness of inventory management practices involves utilizing performance metrics such as inventory turnover ratio, order accuracy, and carrying costs. By establishing key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can evaluate their current inventory processes and identify areas for enhancement. For instance, a high inventory turnover ratio may indicate efficient stock movement while also highlighting opportunities to reduce excess carrying costs. Regularly reviewing these metrics provides valuable insights into operational performance, thereby allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions.
Moreover, assessing customer feedback plays a pivotal role in the adaptation of inventory strategies. Organizations that actively seek and analyze customer input surrounding product availability and delivery satisfaction can recalibrate their inventory management to better align with consumer expectations. Additionally, it is essential to keep a pulse on market trends and shifts in customer preferences. By integrating real-time data analytics, businesses can identify the optimal stock levels and adapt their procurement strategies, thus improving responsiveness to fluctuations in demand.
Approaching inventory management as an ongoing process rather than a one-time setup fosters agility and resilience within a business. The iterative cycle of reviewing performance, incorporating feedback, and adapting strategies will cultivate a more robust inventory system. As companies commit to these continuous improvement practices, they position themselves to thrive in an ever-changing market environment, facilitating sustained growth and customer satisfaction.